Introduction
Do you frequently deal with sneezing, itchy skin, watery eyes, or unexplained rashes? Do certain seasons, foods, or environments seem to trigger uncomfortable symptoms? If so, you might be one of the millions of people affected by allergies, and you’re not alone.
While some allergic reactions are mild and manageable, others can severely impact your daily life. The key to relief often begins with allergy testing, a diagnostic tool designed to help you identify what’s triggering your symptoms. With the right diagnosis, you can take control of your health and minimize the effects of allergens.
What Is Allergy Testing?
Allergy testing is a medical process used to identify substances—called allergens—that cause allergic reactions in your body. When you come into contact with an allergen, your immune system mistakenly sees it as a threat and overreacts, producing symptoms like hives, sneezing, or difficulty breathing.
Common allergens include:
- Pollen
- Dust mites
- Pet dander
- Mold
- Certain foods (e.g., peanuts, dairy, shellfish)
- Insect stings
- Medications
- Latex
Allergy testing helps pinpoint which specific allergens are causing your symptoms, so your healthcare provider can tailor a treatment plan that works.
Why Is Allergy Testing Important?
Many people spend years guessing what they’re allergic to—removing foods, changing detergents, or staying indoors during spring. While some of these efforts may help, they often rely on trial and error, leading to frustration and continued discomfort.
Here’s why accurate allergy testing is crucial:
- Precise identification: Know exactly what’s causing your symptoms
- Avoid unnecessary restrictions: No need to cut out foods or avoid pets unless necessary
- Improved treatment: Enables targeted therapies like antihistamines or immunotherapy
- Emergency prevention: Helps avoid serious allergic reactions like anaphylaxis
Allergy testing takes the guesswork out of the equation and gives you clarity, control, and confidence in managing your health.
Who Should Get Allergy Testing?
You should consider allergy testing if you experience:
- Chronic or seasonal sneezing, nasal congestion, or a runny nose
- Skin conditions like eczema or chronic hives
- Asthma symptoms triggered by environmental factors
- Gastrointestinal issues after eating certain foods
- Reactions like swelling or itching after insect stings or medications
- Anaphylactic reactions without a known cause
Children, teens, and adults can all benefit from allergy testing, especially if symptoms interfere with sleep, work, school, or everyday activities.
Types of Allergy Tests
There are several types of allergy tests, and the right one depends on your symptoms, medical history, and suspected allergens.
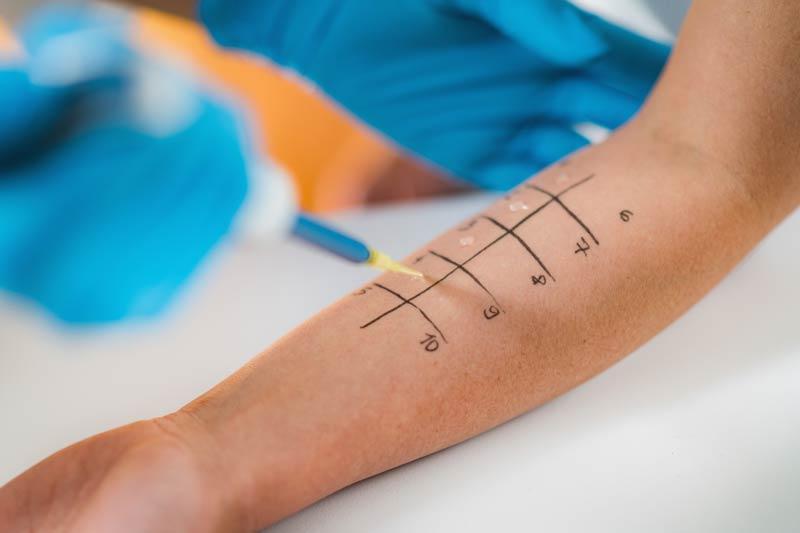
1. Skin Prick Test (SPT)
- A small amount of allergen is placed on your skin (usually the forearm or back)
- The skin is lightly pricked so the allergen can enter the top layer
- If a red, raised bump appears within 15–20 minutes, it indicates a positive reaction
Best for: Pollen, dust, mold, pet dander, food, and insect venom allergies
Pros: Fast, affordable, and widely available
2. Intradermal Skin Test
- A small amount of allergen is injected just under the skin
- More sensitive than the skin prick test
Best for: Detecting allergies to insect venom or medications
Note: Slightly higher risk of false positives
3. Blood Tests (IgE Testing)
- Measures the level of allergen-specific antibodies (IgE) in the blood
- No exposure to allergens is required
Best for: People with skin conditions, those on certain medications, or at high risk of severe reactions
Drawback: Results take a few days and may be less specific than skin tests
4. Patch Testing
- Used to identify delayed allergic reactions, especially those causing skin rashes
- Small patches containing allergens are placed on the skin and left for 48 hours
Best for: Contact dermatitis caused by metals, cosmetics, latex, or chemicals
5. Oral Food Challenge (OFC)
- Patient consumes small amounts of a suspected food under close medical supervision
- Considered the most accurate test for food allergies
Best for: Confirming or ruling out specific food allergies
Risk: Must be done in a controlled setting due to the potential for severe reactions
What to Expect During Allergy Testing
Before the Test:
- You may be asked to stop taking antihistamines for a few days
- Provide a full medical and symptom history
- Bring a list of medications and any suspected allergens
During the Test:
- The process usually takes 20–60 minutes, depending on the type of test
- You may feel mild discomfort (itching or tingling) if you react to a substance
After the Test:
- Your doctor will review the results and explain which substances triggered a reaction
- A personalized treatment plan will be created based on your results
Treatment Options After Allergy Testing
Once your allergens are identified, your provider may recommend:
1. Avoidance
- Reducing exposure to known allergens (e.g., using air filters, changing diet, keeping pets out of bedrooms)
2. Medications
- Antihistamines
- Nasal sprays
- Corticosteroids
- Decongestants
- Epinephrine auto-injectors for severe allergies
3. Allergy Immunotherapy
- Gradual exposure to allergens via shots or tablets
- Helps desensitize your immune system over time
- May reduce symptoms or eliminate allergy altogether
Final Thoughts
Allergies can disrupt your life in subtle and significant ways—from persistent sniffles and rashes to dangerous reactions that require emergency care. The good news? You don’t have to live in fear or frustration. Allergy testing is the first and most powerful step toward understanding your triggers and reclaiming your health.